Research
Our Research
The DIMMS Lab employs a multidisciplinary approach to understand disease dynamics through advanced mathematical modeling, statistical analysis, and machine learning. Our work bridges molecular-level interactions to population-scale epidemiology, informing public health strategies and clinical decisions.
Research Areas
Multi-timescale Analysis
Analyzing disease processes across multiple timescales—from rapid molecular interactions to long-term population dynamics. We develop mathematical frameworks that bridge molecular, cellular, individual, and population-level dynamics.
Immunity System Modeling
Developing sophisticated models of immune response dynamics to understand how pathogens interact with host immunity. Our research encompasses antibody responses, T-cell dynamics, and cytokine signaling networks.
Spatial Epidemiology
Examining how geographical and socioeconomic factors influence disease transmission and outcomes. We integrate spatial statistics with epidemiological models to identify risk factors and predict disease spread patterns.
Statistical Methods & Machine Learning
Employing advanced statistical frameworks and machine learning techniques including Bayesian inference, time series analysis, deep neural networks, and random forests for epidemiological data analysis.
Neural Network Disease Prediction
Pioneering disease-informed neural networks that combine epidemiological principles with deep learning architectures. These hybrid models enhance prediction accuracy for outbreak forecasting and disease progression.
Mathematical Biology
Developing robust mathematical models for public health and policy applications, including nonlinear dynamical systems analysis, disease modeling using ODEs, and vaccination strategy optimization.
How Our Research Connects
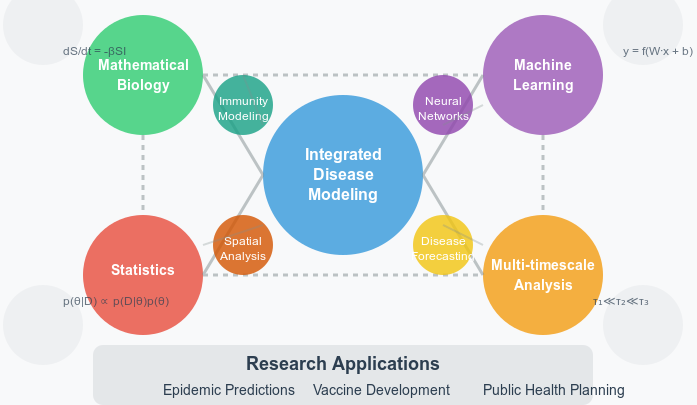
Our research areas are deeply interconnected, with insights from one domain informing and enhancing work in others. This integrated approach allows us to tackle complex health challenges from multiple angles.
Research Applications
Our research directly impacts real-world health outcomes through:
Current Projects
Dengue Virus-Immune System Interactions
ActiveModeling dengue virus interactions with the immune system to understand disease severity and develop better treatment strategies.
Mpox Spatial Distribution in Ontario
ActiveMapping geographical distribution and analyzing socio-environmental indicators associated with Mpox risk in Ontario.
Avian Influenza Prediction Networks
ActiveDeveloping neural networks for predicting avian influenza spread using clinical, genomic, environmental, and demographic data.
Vaccination Strategy Optimization
ActiveMathematical modeling of vaccination strategies to optimize coverage and long-term effectiveness across populations.
Deep Learning for Epidemiological Analysis
ActiveApplying deep neural networks and random forests to extract meaningful patterns from complex epidemiological datasets.
Collaborative Research
Our research benefits from international collaborations and interdisciplinary partnerships:
International Networks
Collaborations with researchers in Nigeria, Pakistan, Iraq, and Bahrain
Interdisciplinary Approach
Integration of mathematics, biology, computer science, and public health
Industry Partnerships
Working with health organizations on real-world applications
Academic Collaborations
Partnerships with institutions worldwide for comprehensive research
